Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Engineering Research Center of Precision Photonics Integration and System Application, Ministry of Education & Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Manipulation, Ministry of Education & National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures & College of Engineering and Applied Sciences & Institute of Optical Communication Engineering & Nanjing University-Tongding Joint Lab for Large-Scale Photonic Integrated Circuits, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
2 College of Electronics and Optical Engineering and College of Flexible Electronics, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
3 The 41st Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corp, Qingdao 266000, China
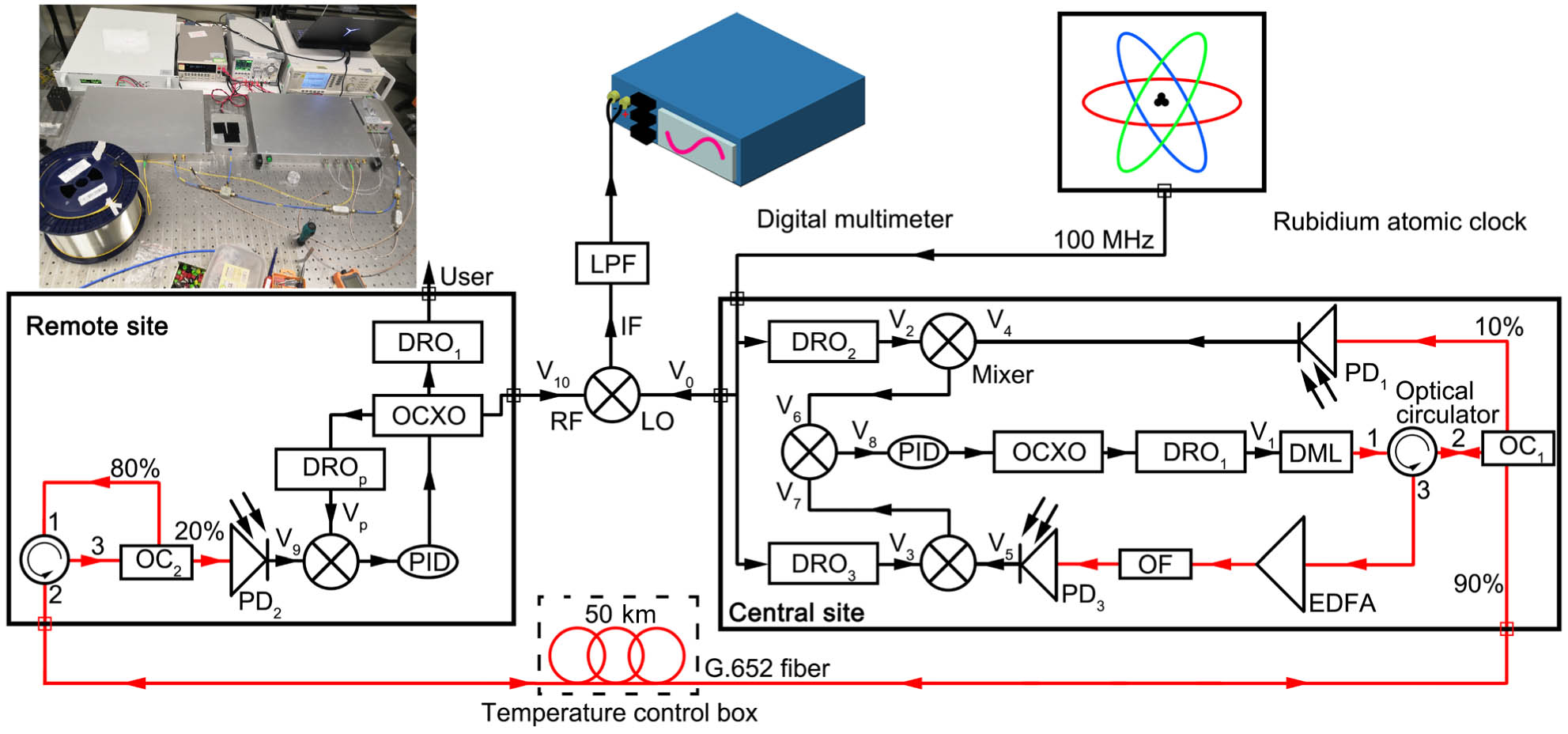
The stable long-distance transmission of radio-frequency (RF) signals holds significant importance from various aspects, including the comparison of optical frequency standards, remote monitoring and control, scientific research and experiments, and RF spectrum management. We demonstrate a scheme where an ultrastable frequency signal was transmitted over a 50 km coiled fiber. The optical RF signal is generated using a two-section distributed feedback (DFB) laser for direct modulation based on the reconstruction equivalent chirp (REC) technique. The 3-dB modulation bandwidth of the two-section DFB laser is 18 GHz and the residual phase noise of is achieved at 10-Hz offset frequency. We report a short-term stability of at an average time of 1 s and a long-term stability of at the measurement time of 62,000 s when applying current to the front section of the DFB laser. By applying power to both sections, the stability of the system improves to within a testing period of 56,737 s. Despite applying temperature variations to the transmission link, long-term stability of at 23.9 h can still be achieved.
frequency dissemination two-section DFB laser phase stability Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(1): 013903

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic and Optical Engineering and College of Flexible Electronics (Future Technology), Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
2 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
3 College of Communications Engineering, PLA Army Engineering University, Nanjing 210007, China
Modulation bandwidth enhancement in a directly modulated two-section distributed feedback (TS-DFB) laser based on a detuned loading effect is investigated and experimentally demonstrated. The results show that the 3-dB bandwidth of the TS-DFB laser is increased to 17.6 GHz and that chirp parameter can be reduced to 2.24. Compared to the absence of a detuned loading effect, there is a 4.6 GHz increase and a 2.45 reduction, respectively. After transmitting a 10 Gb/s non-return-to-zero (NRZ) signal through a 5-km fiber, the modulation eye diagram still achieves a large opening. Eight-channel laser arrays with precise wavelength spacing are fabricated. Each TS-DFB laser in the array has side mode suppression ratios (SMSR) > 49.093 dB and the maximum wavelength residual < 0.316 nm.
distributed feedback (DFB) laser detuned loading effect direct modulation Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(11): 112301
1 南京邮电大学电子与光学工程学院、柔性电子(未来技术)学院,江苏 南京 210023
2 南京大学现代工程与应用科学学院,江苏 南京 210093
3 中国卫星海上测控部,江苏 江阴 214431
4 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学通信工程学院,江苏 南京 210007
双波长激光器腔内模式竞争激烈,因此输出模式的稳定性是双波长激光器的关键参数。从降低双波长激光器中两个主模之间的功率差、提高边模抑制比出发,设计了集成反射区的两段式双波长分布反馈半导体激光器。利用传输矩阵法对激光器的光栅结构进行仿真,分析了反射区光栅对激光器的阈值、主模功率差等参数的影响。根据仿真优化的结果,制作了单片集成两段式双波长分布反馈半导体激光器芯片并进行了测试。测试结果表明两段式结构能够提高双波长激光器的稳定性和边模抑制比,减小两个主模的功率差。在稳定工作的情况下,两个主模功率差可达0.3 dB,边模抑制比大于35 dB。
激光器 双波长激光器 分布反馈半导体激光器 两段式激光器 光子集成 单片集成 光学学报
2023, 43(10): 1014002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Communications Engineering, Army Engineering University of PLA, Nanjing 210007, China
2 School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
3 Microwave-Photonics Technology Laboratory, National Laboratory of Microstructures & College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
Weak RF signal detection with high resolution and no blind zone based on directly modulated multi-mode optoelectronic oscillation has been proposed. The high-sensitivity optical modulators and optical filters are avoided because multi-mode oscillation is obtained based on directly modulating the semiconductor laser at the relaxation oscillation frequency. For the directly modulated optoelectronic oscillator, the detection characteristics such as gain for the RF signal, resolution, noise floor, and sensitivity are firstly analyzed. The experimental results are consistent with the simulated results. For the RF signal of unknown frequency, it can be detected out and amplified by tuning the bias current and delay time of the loop. There is no blind zone within 1–4.5 GHz. The system provides a maximum gain of 17.88 dB for the low-power RF signal. The sensitivity of the system can reach as high as . The properties such as gain dynamic range and power stability are also investigated. The system has potential for weak RF signal detection, especially for the RF signal with unknown frequency.
radio frequency detection optoelectronic oscillator distributed feedback semiconductor laser Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(11): 113901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
3 Photonics Information Technology Laboratory, Institute of Communication Engineering, Army Engineering University of PLA, Nanjing 210007, China
We demonstrate a high-resolution frequency-modulated continuous-wave dual-frequency LIDAR system based on a monolithic integrated two-section (TS) distributed feedback (DFB) laser. In order to achieve phase locking of the two lasers in the TS-DFB laser, the sideband optical injection locking technique is employed. A high-quality linear frequency-modulated signal is achieved from the TS-DFB laser. Utilizing the proposed LIDAR system, the distance and velocity of a target can be measured accurately. The maximum relative errors of distance and velocity measurement are 1.6% and 3.18%, respectively.
dual-frequency LIDAR integrated two-section DFB laser frequency-modulated continuous wave linear frequency modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(11): 111402
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Shenzhen Research Institute, Xiamen University, Shenzhen 518057, China
3 Analysis and Test Center of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610000, China
We report on diode-pumped continuous-wave Pr-doped yttrium lithium fluoride (Pr:YLF) laser and its frequency doubling to 320 nm. The maximum output power of the 640 nm fundamental wave reached 3.44 W with a slope efficiency of about 48.3%. Using a type-I phase-matched lithium triborate (LBO) crystal as a frequency doubler, we have achieved 320 nm ultraviolet radiation with a maximum output power of 1.01 W, which is the highest power ever reported under diode pumping, to the best of our knowledge.
Pr:YLF crystal frequency doubling ultraviolet continuous wave Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(9): 091406

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Materials and Devices, School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou 221116, China
3 School of Physics Science and Engineering, Institute for Advanced Study, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
4 Department of Physics, Sofia University, 5 James Bourchier Blvd., 1164 Sofia, Bulgaria
5 e-mail: xdxu79@jsnu.edu.cn
We report on a diode-end-pumped high-power and high-energy Nd:YAG single-crystal fiber laser at 1834 nm. Two 808 nm diodes injecting about 58 W pump power into the Nd:YAG fiber have generated 3.28 W continuous-wave and 1.66 W Cr:ZnSe-based passively Q-switched lasers. Slope efficiencies with respect to pump powers are 8.7% for the continuous-wave laser and 4.9% for the Q-switched laser. The extracted maximum pulse energy is about 266.9 μJ, and the corresponding maximum pulse peak power is 2.54 kW. These performances greatly surpass previous results regarding this specific laser emission because the laser gain medium in the form of fiber can significantly mitigate thermally induced power saturation thanks to its significantly reduced thermal lensing effect. Single-crystal fiber lasers show great potential for high average power, pulse energy, and peak power.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(2): 02000162

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Microwave-Photonics Technology Laboratory, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
We review the recent work of distributed-feedback (DFB) multi-wavelength semiconductor laser arrays (MWLAs) based on the reconstruction equivalent chirp (REC) technique. The experimental results show that the proposed MWLA has very high wavelength precision (<±0.1 nm), while the fabrication cost is low. Only one step of holographic exposure and another step of photolithography are required for grating fabrication. The packaging technique for a high-bandwidth analog DFB laser and laser array was developed. A directly modulated MWLA transmitter module was achieved. In addition, an improved MWLA with an integrated reflector was proposed and successfully applied in a radio-over-fiber system.
140.2010 Diode laser arrays 050.2770 Gratings Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010005
School of Opto-Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2011, 4(4): 411
设计了一台高能量输出的电光调Q脉冲串Nd∶YAG激光器, 可以对脉冲串重复频率、脉冲数目、脉冲间隔进行调节。重复频率1~10Hz, 每一个脉冲串含有1~3个脉, 其间隔大于200μs可调。采用平凸腔的结构, 对一定重频下的热透镜效应进行补偿。典型的实验结果为:当重频为10Hz、脉冲间隔为548μs时, 三脉冲最大输出能量608mJ, 双脉冲最大能量输出405mJ, 单脉冲最大输出能量为200mJ, 其中单个脉冲的脉宽约为8ns, 发散角为3.4mrad。
激光技术 脉冲串 可调 电光调Q laser techniques multi-pulsed modulation electroic-optical Q-switch





